Índice
- ¿Qué es una válvula de mariposa?
- ¿Cómo funciona una válvula de mariposa?
- Componentes clave de una válvula de mariposa
- Tipos de válvulas de mariposa
- Tipos de conexión de las válvulas de mariposa
- Materiales y temperaturas
- Aplicaciones y casos prácticos
- Opciones de actuación
- Ventajas y desventajas
- Criteria de selección
- Mantenimiento y resolución de problemas
- Reflexiones finales
¿Qué es una válvula de mariposa?
Una válvula de mariposa es una válvula de un cuarto de vuelta que controla el caudal de fluido mediante un disco giratorio. Cuando el disco gira 90 grados, abre o cierra completamente el flujo. Es como una compuerta circular que se abre y se cierra dentro de una tubería.
Bastante sencillo, ¿verdad?
Pero aquí está la cosa:
Aunque las válvulas de mariposa tienen un diseño sencillo, son INCREÍBLEMENTE versátiles. Se utilizan en todas partes, desde plantas de tratamiento de agua hasta instalaciones de procesamiento químico.
De hecho, las válvulas de mariposa son uno de los tipos de válvula más populares en las aplicaciones industriales actuales.
¿Por qué?
Porque son compactas, rentables y muy fáciles de manejar.
En esta guía, voy a desglosar todo lo que necesitas saber sobre válvulas mariposa. Cómo funcionan, los distintos tipos y cuándo se deben (y cuándo no) utilizar.
Vamos a sumergirnos.
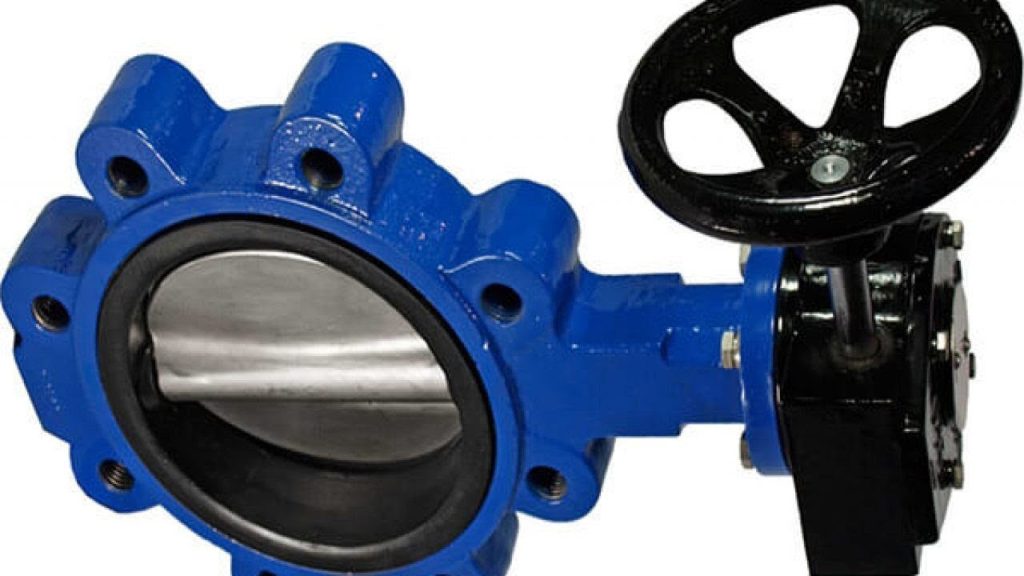

¿Cómo funciona una válvula de mariposa?
El principio de funcionamiento de una válvula de mariposa es bastante sencillo.
Así es como funciona:
Una válvula de mariposa tiene un disco circular montado sobre un eje giratorio (llamado vástago). Al girar la maneta o el actuador, el vástago hace girar el disco.
¿Cuando el disco está paralelo al flujo? La válvula está totalmente abierta.
¿Cuando el disco está perpendicular al flujo? La válvula está completamente cerrada.
Y escucha esto:
Basta con girar la maneta 90 grados para pasar de totalmente abierta a totalmente cerrada. Por eso las válvulas de mariposa se llaman "válvulas de cuarto de vuelta".
Pero aquí es donde se pone interesante:
También puede colocar el disco en diferentes ángulos para controlar el caudal. ¿Desea un caudal 50%? Coloque el disco a unos 45 grados. ¿Sólo necesita un chorrito? Ábralo ligeramente.
Esta capacidad de estrangulación hace que las válvulas de mariposa sean muy versátiles para aplicaciones de control de caudal.
¿En resumidas cuentas?
Las válvulas de mariposa ofrecen un control de caudal sencillo y fiable con un mínimo de piezas móviles. Por eso son tan populares en aplicaciones industriales.
Componentes clave de una válvula de mariposa
Cada válvula de mariposa tiene cuatro componentes principales que trabajan juntos. Permítame que se los desglose:
1. Cuerpo de la válvula
El cuerpo de la válvula es la carcasa principal que contiene todas las piezas internas. Suele estar fabricado con materiales resistentes, como hierro fundido o acero inoxidable.
El cuerpo se conecta al sistema de tuberías y protege el disco y otros componentes de posibles daños.
Piense que es la coraza protectora de la válvula.
2. Disco
El disco es la estrella del espectáculo. Es la placa redonda la que realmente controla el flujo.
Al girar el disco, éste bloquea el paso del caudal (cerrado) o se alinea con él (abierto).
Aquí hay algo genial:
El disco permanece siempre en el paso del caudal, incluso cuando está totalmente abierto. Esto crea una ligera caída de presión, pero también significa que la válvula puede responder instantáneamente a los cambios de control.
3. Vástago
El vástago conecta el disco a la empuñadura externa o al actuador. Al girar la empuñadura, el vástago hace girar el disco.
La mayoría de los vástagos atraviesan el cuerpo de la válvula y están sellados con juntas tóricas para evitar fugas.
Algunas válvulas utilizan un vástago de una pieza. Otras utilizan un diseño de dos piezas para facilitar el mantenimiento.
4. Asiento
El asiento es la superficie de sellado contra la que cierra el disco. Es lo que impide las fugas cuando la válvula está cerrada.
Hay dos tipos principales de asientos:
- Asientos blandos (de caucho o PTFE) para un cierre hermético
- Asientos metálicos para aplicaciones de alta temperatura
El material del asiento suele determinar la temperatura y la presión nominales de la válvula.
Tipos de válvulas de mariposa
No todas las válvulas de mariposa son iguales. Existen varios diseños diferentes, cada uno con sus propias ventajas.
Le explicaré los principales tipos:
Válvulas de mariposa de desplazamiento cero (concéntricas)
Las válvulas de offset cero son el diseño más sencillo. El vástago pasa directamente por el centro del disco.
Estas válvulas utilizan un asiento de goma blanda que envuelve el borde del disco. Al cerrarse, el disco comprime el asiento para conseguir un cierre hermético.
Lo mejor para:
- Aplicaciones de baja presión (hasta 250 PSI)
- Servicio de agua y aire
- Proyectos con presupuesto ajustado
Inconvenientes: El disco roza constantemente contra el asiento, lo que puede causar desgaste con el tiempo.
Válvulas de mariposa de doble offset (alto rendimiento)
Las válvulas de doble desplazamiento tienen dos desplazamientos del vástago:
- El vástago está desplazado de la línea central del disco
- El vástago está desplazado de la línea central del tubo
Este diseño reduce el desgaste del asiento porque el disco se "levanta" del asiento durante la apertura.
Lo mejor para:
- Mayores presiones y temperaturas
- Se necesita una vida útil más larga
- Aplicaciones de procesamiento químico
Válvulas de mariposa de triple offset
Las válvulas de triple desplazamiento añaden un tercer desplazamiento: un desplazamiento angular en el cono de sellado.
He aquí por qué es importante:
El disco sólo entra en contacto con el asiento en el momento del cierre completo. Cero fricción durante el funcionamiento significa prácticamente ningún desgaste.
Lo mejor para:
- Temperaturas y presiones extremas
- Servicio de vapor
- Aplicaciones sin fugas
- Control de procesos críticos
¿La contrapartida? Las válvulas de triple offset cuestan bastante más que otros tipos.
Tipos de conexión de las válvulas de mariposa
La forma de conectar una válvula de mariposa a su sistema de tuberías es importante. Y mucho.
Estos son los principales tipos de conexión:
Estilo oblea
Las válvulas de mariposa wafer encajan entre dos bridas de tubería. Los pernos largos atraviesan las bridas y sujetan la válvula en su sitio.
Pros:
- Diseño compacto
- Ligero
- Económico
Contras:
- No se puede utilizar para el servicio de fin de línea
- Requiere la parada del sistema para su mantenimiento
Estilo
Las válvulas Lug tienen orificios roscados alrededor del cuerpo. Cada brida de tubo se atornilla directamente a la válvula.
Gran ventaja: Puede desconectar un lado de la tubería sin quitar la válvula.
Esto hace que las válvulas de orejeta sean perfectas para:
- Servicio de fin de línea
- Aplicaciones que necesitan capacidad de aislamiento
- Sistemas que requieren un mantenimiento frecuente
Brida
Las válvulas de mariposa con bridas tienen caras elevadas en ambos lados que coinciden con las bridas de tubería estándar.
Cuándo utilizarlos:
- Tuberías de gran diámetro
- Sistemas de alta presión
- Cuando se necesita la máxima estabilidad
Soldadura a tope
Estas válvulas se sueldan directamente a la tubería. No necesitan bridas.
Perfecto para:
- Instalaciones permanentes
- Servicio de alta presión/alta temperatura
- Aplicaciones en las que no pueden producirse fugas
¿El inconveniente? Son difíciles de quitar para su mantenimiento.
Materiales y temperaturas
Los materiales utilizados en la construcción de las válvulas de mariposa influyen directamente en el rendimiento y la vida útil.
Permítanme desglosar las opciones más comunes:
Materiales de la carrocería
Hierro fundido
- Temperatura: de -20°F a 450°F
- Bueno para el servicio de agua y aire
- Opción rentable
Acero carbono
- Temperatura: de -20°F a 800°F
- Soporta presiones más elevadas que la fundición
- Común en aplicaciones de petróleo y gas
Acero inoxidable (316/316L)
- Gama de temperaturas: -320 °F a 1000 °F
- Excelente resistencia a la corrosión
- Ideal para la industria química y alimentaria
Hastelloy/Inconel
- Resistencia a temperaturas extremas y a la corrosión
- Utilizado en servicios químicos altamente agresivos
- Precio elevado
Los materiales de los asientos y sus límites
El material del asiento suele determinar la temperatura nominal de la válvula:
EPDM (etileno propileno)
- Gama: de -20°F a 250°F
- Excelente para el servicio de agua
- No es compatible con aceites ni hidrocarburos
Buna-N (nitrilo)
- Intervalo: de -35 °F a 250 °F
- Bueno para aceites y combustibles
- No apto para oxidantes fuertes
PTFE (teflón)
- Gama: de -100°F a 450°F
- Resistencia química universal
- Mayor coste pero mayor vida útil
Asientos metálicos
- Alcance: Hasta 1000°F+
- Para temperaturas extremas
- Puede tener ligeras fugas
Aplicaciones y casos prácticos
Las válvulas de mariposa se utilizan en multitud de sectores. Estos son los sectores en los que suelen encontrarse:
Tratamiento de aguas y aguas residuales
Este es probablemente el mayor mercado para las válvulas de mariposa.
¿Por qué?
Porque manejan grandes caudales con eficacia y resisten la corrosión habitual en el tratamiento del agua.
Aplicaciones habituales:
- Toma de agua bruta
- Red de distribución
- Aislamiento de la bomba
- Sistemas de lavado a contracorriente
Sistemas HVAC
Los sistemas mecánicos de los edificios adoran las válvulas de mariposa para el control del agua fría y caliente.
Son perfectos aquí porque:
- Tamaño compacto que cabe en salas de máquinas estrechas
- Accionamiento rápido para el control de la temperatura
- Rentable para tubos de gran tamaño
Procesado químico
Las plantas químicas utilizan válvulas de mariposa para:
- Control de alimentación del reactor
- Aislamiento de tanques de almacenamiento
- Servicio corrosivo (con materiales adecuados)
¿La clave? Seleccionar los materiales adecuados para la compatibilidad química.
Alimentos y bebidas
Las válvulas de mariposa sanitarias son enormes en el procesado de alimentos.
Cuentan con:
- Superficies pulidas para facilitar la limpieza
- Aprobado por la FDA materiales
- Capacidad CIP (limpieza in situ)
Generación de energía
Las centrales eléctricas utilizan válvulas de mariposa para:
- Sistemas de agua de refrigeración
- Servicio de condensado de vapor
- Sistemas de manipulación de cenizas
Opciones de actuación
El funcionamiento de una válvula de mariposa depende de las necesidades de su aplicación.
Estas son sus principales opciones:
Funcionamiento manual
Palanca
- Se utiliza en válvulas más pequeñas (normalmente de 2 a 6 pulgadas)
- Funcionamiento rápido
- Indicación visual de posición
Operador de engranajes
- Para válvulas más grandes o aplicaciones de alto par
- Proporciona ventajas mecánicas
- El tornillo sin fin autobloqueante evita movimientos no deseados
Funcionamiento automatizado
Actuadores eléctricos
- Control preciso de la posición
- Fácil integración con los sistemas de control
- Requiere fuente de alimentación
- Lo mejor para: Uso frecuente, necesidades de control remoto
Actuadores neumáticos
- Funcionamiento rápido (normalmente 1-2 segundos)
- Opciones de seguridad disponibles
- Requiere aire comprimido
- Lo mejor para: Aplicaciones de seguridad, ciclismo frecuente
Actuadores hidráulicos
- Capacidad de par extremadamente alta
- Buen funcionamiento
- Lo mejor para: Válvulas grandes, sistemas de alta presión
Ventajas y desventajas
Seamos realistas sobre los pros y los contras de las válvulas de mariposa.
Ventajas
1. Diseño compacto
Las válvulas de mariposa ocupan mucho menos espacio que las válvulas de compuerta o de globo. Esto es importante a la hora de diseñar tuberías estrechas.
2. Funcionamiento rápido
El funcionamiento de un cuarto de vuelta permite una apertura y cierre rápidos. Perfecto para el aislamiento de emergencia.
3. Baja caída de presión
Cuando están completamente abiertas, las válvulas de mariposa crean una restricción mínima del caudal.
4. Rentable
Especialmente en tamaños grandes, las válvulas de mariposa cuestan bastante menos que otros tipos de válvulas.
5. Buen control del flujo
El ángulo del disco proporciona una capacidad de estrangulación decente para muchas aplicaciones.
6. Ligero
Más fácil de instalar y requiere menos soporte de tuberías que los tipos de válvula más pesados.
Desventajas
1. Presiones nominales limitadas
La mayoría de las válvulas de mariposa alcanzan un máximo de 250-300 PSI. ¿Necesita más presión? Tendrá que pagar más.
2. No Full Bore
El disco siempre permanece en la trayectoria del flujo, creando cierta restricción.
3. Limitaciones de estrangulamiento
El estrangulamiento a alta velocidad puede dañar el disco y el asiento.
4. No apto para lodos
Los materiales abrasivos pueden erosionar rápidamente las superficies de sellado.
5. Limitaciones de temperatura
Las válvulas de asiento blando tienen restricciones de temperatura basadas en el material del asiento.
Criteria de selección
Elegir la válvula de mariposa adecuada no es una ciencia exacta. Pero hay que tener en cuenta varios factores:
1. Condiciones de servicio
Presión: Asegúrese de que la presión nominal de la válvula supera la presión máxima del sistema.
Temperatura: Compruebe tanto la temperatura de funcionamiento como la temperatura ambiente
Medios de comunicación: Considerar la compatibilidad química con todos los materiales húmedos
2. Requisitos de rendimiento
Pregúntatelo a ti mismo:
- ¿Necesito un cierre hermético?
- ¿Esta válvula acelerará o sólo abrirá/cerrará?
- ¿Con qué frecuencia funcionará?
3. Restricciones de instalación
Considéralo:
- Espacio disponible
- Configuración de tuberías
- Necesidades de acceso para mantenimiento
- Limitaciones de peso
4. 4. Consideraciones económicas
Acuérdate de tenerlo en cuenta:
- Precio de compra inicial
- Gastos de instalación
- Mantenimiento a largo plazo
- Costes energéticos (pérdida de carga)
Mantenimiento y resolución de problemas
Esto es lo que pasa con las válvulas de mariposa:
Requieren muy poco mantenimiento. Pero "poco" no significa "ningún" mantenimiento.
Tareas periódicas de mantenimiento
Trimestral:
- Cicle la válvula para evitar que se atasque
- Comprobación de fugas externas
- Verificar el buen funcionamiento
Anualmente:
- Inspeccionar el estado del asiento
- Comprobar la empaquetadura del vástago
- Lubricar si es necesario
- Pruebe el funcionamiento del actuador (si está automatizado)
Problemas comunes y soluciones
Fuga más allá del asiento
- Causa: Asiento desgastado o dañado
- Reparar: Sustituir el asiento o toda la válvula
Difícil de manejar
- Causa: Corrosión, acumulación de cal o cojinetes dañados.
- Reparación: Limpiar y lubricar, sustituir las piezas desgastadas
Fuga del vástago
- Causa: Empaquetadura o juntas tóricas desgastadas
- Arreglo: apretar la empaquetadura o cambiar las juntas
Problemas con los actuadores
- Causa: Varias (pérdida de potencia, suministro de aire, fallo mecánico)
- Fix: Solución de problemas en función del tipo de actuador
Reflexiones finales
Así que.., ¿qué es una válvula de mariposa?
Se trata de un dispositivo de control de caudal sencillo pero versátil que utiliza un disco giratorio para regular el caudal de fluido. Con una selección y un mantenimiento adecuados, las válvulas de mariposa ofrecen un servicio fiable en innumerables aplicaciones.
¿La clave del éxito?
Comprender sus necesidades específicas y elegir el tipo de válvula, los materiales y las características adecuados para su aplicación.
Tanto si está diseñando un nuevo sistema como actualizando un equipo existente, las válvulas de mariposa ofrecen un excelente equilibrio entre rendimiento, coste y fiabilidad.
Sólo recuerda:
No todas las aplicaciones son adecuadas para una válvula de mariposa. ¿Pero cuando encajan? Son difíciles de superar.
¿Necesita ayuda para elegir la válvula de mariposa adecuada para su aplicación? Tenga en cuenta factores como la presión, la temperatura, la compatibilidad de medios y el rendimiento requerido. Y no dude en consultar a los fabricantes o ingenieros de válvulas para aplicaciones críticas.
Porque, al fin y al cabo, la elección de la válvula correcta puede marcar la diferencia entre un sistema que funcione sin problemas durante años y otro que cause constantes dolores de cabeza.