Quelle est la fonction d'un clapet anti-retour? Ces héros méconnus empêchent les défaillances catastrophiques des systèmes, de la plomberie de votre maison aux réacteurs nucléaires. Voyons comment ce simple dispositif protège les équipements, permet d'économiser des millions de dollars de dommages et pourquoi 92% des ingénieurs industriels les considèrent comme des éléments non négociables pour l'intégrité des systèmes.
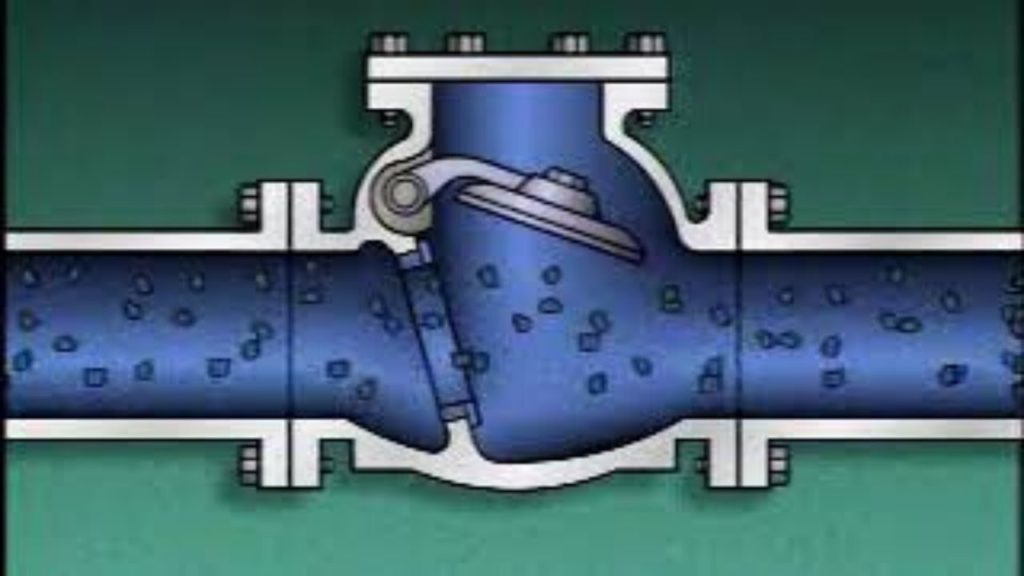
Table des matières
- Fonctionnement des clapets anti-retour : Le gardien automatique
- 5 fonctions critiques à ne pas négliger
- Types de clapets de retenue : Une solution adaptée à votre mission
- Les applications industrielles permettent d'économiser des millions d'euros
- Éviter les erreurs coûteuses : 4 règles de sélection
- Pourquoi les clapets anti-retour survivent-ils aux autres composants ?
- Le bilan
Fonctionnement des clapets anti-retour : Le gardien automatique
Lorsque le fluide s'écoule correctement, la valve reste ouverte. Vous inversez le flux ? Elle se ferme instantanément. Pas d'intervention humaine. Pas de source d'énergie. Juste de la physique.
Mécanisme de base :
- Pression différentielle force le mécanisme interne (disque, bille ou diaphragme) à s'ouvrir ou à se fermer
- Pression de fissuration (pression minimale en amont) détermine le seuil d'activation
- Fermeture assistée par gravité/ressort assure un arrêt rapide en cas d'inversion du flux
C'est un peu comme un videur de boîte de nuit pour les pipelines, qui n'autorise qu'un seul sens de circulation.
5 fonctions critiques à ne pas négliger
- Prévention des retours d'eau
L'écoulement inverse peut détruire les pompes, contaminer les réserves d'eau ou déclencher des réactions chimiques. Les clapets anti-retour bloquent cette menace insidieuse. Exemple : Les réseaux d'eau municipaux les utilisent pour séparer l'eau traitée de l'eau brute, évitant ainsi une contamination croisée mortelle. - Protection de l'équipement
Les compresseurs coûtant plus de $500k implosent lorsque le gaz reflue. Les clapets anti-retour les en empêchent :- Rotation inverse des pompes
- Choc thermique dans les chaudières dû à l'intrusion d'eau froide
- Refoulement dans les conduites de carburant (l'une des principales causes d'incendie dans l'industrie)
- Maintien de la pression
Les gratte-ciel s'appuient sur des clapets anti-retour superposés pour maintenir la pression de l'eau à l'étage supérieur lorsque les pompes s'arrêtent. Sans ces clapets ? Les toilettes ne tireraient pas la chasse d'eau au-delà du 10e étage. - Atténuation des coups de bélier
La fermeture soudaine d'une vanne crée des ondes de choc qui font éclater les canalisations. Non-slam Les clapets anti-retour avec commandes d'amortissement se ferment progressivement, dissipant les coups de bélier de plus de 200 PSI. - Contrôle des contaminations
Dans la fabrication de produits pharmaceutiques, les clapets anti-retour à membrane maintiennent des conditions stériles en empêchant l'inversion du flux unidirectionnel. Une faille pourrait mettre au rebut le $2M dans les vaccins.
Types de clapets de retenue : Une solution adaptée à votre mission
| Type | Meilleur pour | Un avantage unique |
|---|---|---|
| Contrôle de l'oscillation | Gros tuyaux, systèmes d'égouts | Débit intégral ; traite les débris |
| Contrôle de l'ascenseur | Vannes à vapeur haute pression | Joint d'étanchéité assisté par ressort |
| Contrôle de la bille | Boues, opérations minières | Autonettoyant ; fonctionne avec les particules |
| Contrôle de la membrane | Dispositifs médicaux, laboratoires | Fermeture étanche à la bulle ; aucune fuite |
| Vérification des plaquettes | Systèmes CVC à espace restreint | Conception compacte ; temps de réaction rapide |
Conseil de pro : Les vannes à ressort sont plus performantes que les modèles dépendant de la gravité dans les conduites verticales. Il faut toujours tenir compte de l'orientation lors de l'installation.
Les applications industrielles permettent d'économiser des millions d'euros
- Oléoducs et gazoducs : Empêche le refoulement des réservoirs sur des réseaux de 10 000 miles. Sans eux, une simple défaillance de la pompe peut entraîner le drainage d'une ligne entière.
- Centrales électriques : Stoppe l'écoulement inverse des condensats dans les turbines (évite d'endommager les pales $1M+)
- Aérospatiale : Les clapets anti-retour du carburant garantissent que les moteurs ne reçoivent que du propergol circulant vers l'avant.
- Ventilateurs médicaux : Des micro-vannes de contrôle régulent la direction de l'oxygène avec un temps de réponse de 0,001 s.
Alerte 2025 : Les vannes intelligentes de nouvelle génération, équipées de capteurs de pression, prévoient désormais les défaillances avant que les fuites ne se produisent, ce qui permet d'économiser 37% en coûts de maintenance (Per Tech Industrial Journal).
Éviter les erreurs coûteuses : 4 règles de sélection
- Limites de pression et de température
Les systèmes à vapeur nécessitent des clapets de levage conçus pour une température supérieure à 600°F. Les fluides cryogéniques nécessitent des alliages spéciaux. - Compatibilité avec les fluides
Les robinets à tournant sphérique excellent avec les produits chimiques corrosifs. Évitez les clapets à battant dans les milieux caustiques, car les charnières se corrodent. - Vitesse d'écoulement
Les lignes à grande vitesse nécessitent des contrôles de buses pour éviter le battement des disques. Faible débit ? Optez pour des conceptions à faible pression de fissuration. - Réalité de l'entretien
Les contrôles de l'oscillation nécessitent des inspections fréquentes des charnières. Les contrôles des boules ? Ils ne nécessitent pratiquement pas d'entretien mais coûtent 20% de plus.
Pourquoi les clapets anti-retour survivent-ils aux autres composants ?
Ils ne contiennent pas d'électronique. Pas de logiciel. Juste des pièces usinées avec précision. Avec un entretien approprié :
- Les vannes en acier inoxydable ont une durée de vie de plus de 35 ans dans les systèmes d'eau.
- Les variantes d'alliages de titane résistent à plus de 50 ans dans les plates-formes de forage en mer
Fait amusant : le plus ancien clapet anti-retour encore en service ? Un clapet anti-retour de 1942 dans le métro de Londres, qui protège les trains des inondations depuis la Seconde Guerre mondiale.
Le bilan
Quelle est la fonction d'un clapet anti-retour ? En fin de compte, il s'agit de la sécurité intégrée de votre système contre le chaos. Qu'il s'agisse de prévenir les inondations dans les sous-sols ou de maintenir la stabilité des réacteurs nucléaires, ce dispositif discret fait ce que les opérateurs humains ne peuvent pas faire : réagir instantanément aux flux inversés. Oubliez les technologies sophistiquées : parfois, ce sont les solutions les plus simples qui sauvent le plus de vies et de moyens de subsistance. Alors que les systèmes de fluides deviendront plus intelligents en 2025, le clapet anti-retour reste le gardien mécanique que nous ne pouvons pas contourner.