Já se perguntou porque é que os seus canos de água fazem aqueles ruídos estranhos?
Ou porque é que o seu sistema de rega perde subitamente pressão?
A questão é a seguinte: provavelmente tem um problema de ar. E é exatamente aí que entram as válvulas de ar.

Índice
- O que é uma válvula de ar
- Porque é que as válvulas de ar são mais importantes do que pensa
- Os 3 tipos de válvulas de ar (e quando utilizar cada uma)
- Onde instalar as válvulas de ar (A abordagem estratégica)
- Como funcionam as válvulas de ar (a explicação simples)
- Problemas comuns das válvulas de ar (e como os resolver)
- Dimensionamento de válvulas de ar (da forma correta)
- Melhores práticas de instalação
- Manutenção que realmente importa
- Considerações avançadas para 2025
- O custo de errar
- O seu plano de ação
- A linha de fundo
O que é uma válvula de ar
O que é um válvula de ar? É um dispositivo mecânico que controla automaticamente o fluxo de ar em sistemas de tubagem de líquidos. Pense nele como os pulmões do seu sistema de água - libertando o ar preso quando necessário e deixando entrar ar para evitar vácuos perigosos.
Muito simples, não é?
Mas a questão é a seguinte:
Escolher o errado válvula de ar (ou não as utilizar) pode levar a alguns problemas graves. Estamos a falar de danos nos canos, eficiência reduzida e até mesmo falha total do sistema.
Neste guia, como profissional fabricante de válvulas de arVou explicar-vos tudo o que precisam de saber sobre válvulas de ar. Nada de tretas. Apenas informações práticas que pode utilizar de imediato.
Vamos mergulhar no assunto.
Porque é que as válvulas de ar são mais importantes do que pensa
Veja:
A maioria das pessoas não pensa nas válvulas de ar até que algo corra mal.
Grande erro.
Eis o que acontece quando o ar fica preso nos seus canos:
Eficiência reduzida: As bolsas de ar criam bloqueios que obrigam as bombas a trabalhar mais. Já vi o consumo de energia aumentar até 30% em sistemas sem válvulas de ar adequadas.
Martelo hidráulico: Esses sons de pancada? É o golpe de aríete. E não é apenas irritante - pode literalmente destruir os seus canos.
Corrosão: O oxigénio no ar retido acelera a corrosão dos tubos. Um estudo concluiu que os tubos sem válvulas de ar corroem 40% mais rapidamente do que os tubos com ventilação adequada.
Medição imprecisa: As bolsas de ar desorientam os medidores de caudal, conduzindo a erros de faturação e a ineficiências do sistema.
Conclusão?
As válvulas de ar não são opcionais. São essenciais para qualquer sistema de tubagem de líquidos.
Os 3 tipos de válvulas de ar (e quando utilizar cada uma)
Nem todas as válvulas de ar são iguais.
De facto, existem três tipos principais. E cada um tem um objetivo específico:
1. Válvulas de libertação de ar (pequeno orifício)
Estes são os cavalos de batalha do válvula de ar mundo.
As válvulas de libertação de ar libertam continuamente pequenas bolsas de ar de sistemas pressurizados. São perfeitas para remover o ar dissolvido que se separa da água durante o funcionamento normal.
Quando os utilizar: Instale-os nos pontos altos do seu sistema onde o ar se acumula naturalmente.
Dica profissional: Espace-os a cada 800 metros em tubagens longas para um desempenho ótimo.
2. Válvulas de ar e vácuo (orifício grande)
Pense neles como os pesos pesados.
As válvulas de ar e de vácuo tratam grandes volumes de ar durante:
- Enchimento de condutas
- Drenagem do sistema
- Quedas bruscas de pressão
Abrem-se completamente para permitir que o ar entre ou saia rapidamente, evitando a formação de vácuo que poderia colapsar os tubos.
Quando os utilizar: Crítico nas estações de bombagem e em qualquer lugar onde se possa drenar secções de tubos.
3. Válvulas de ar combinadas
Não consegue decidir entre os dois? Compre os dois.
As válvulas combinadas (também designadas por válvulas de duplo orifício) combinam as funções das válvulas de libertação de ar e de ar e vácuo numa única unidade.
Quando os utilizar: São ideais para a maioria das aplicações, especialmente quando não se tem a certeza do tipo de que se necessita.
Onde instalar as válvulas de ar (A abordagem estratégica)
A localização é importante.
Muito.
Se as válvulas de ar forem instaladas no sítio errado, são basicamente decorações caras.
Eis a minha estratégia de colocação comprovada:
Os pontos altos são críticos
O ar é mais leve do que a água. (Obviamente.)
Por isso, sobe para os pontos mais altos do seu sistema. É aí que deve instalar válvulas de ar.
Isto inclui:
- Picos de condutas
- Pontos altos temporários
- Alterações na inclinação
As tubagens longas também precisam de amor
Mesmo em secções relativamente planas, instale válvulas de ar a cada 500-800 metros.
Porquê?
Porque o ar acumula-se à distância. E as pequenas bolhas combinam-se em bolsas de ar maiores e mais problemáticas.
Depois dos dispositivos de controlo do caudal
As bombas, válvulas e limitadores de caudal criam turbulência.
Turbulência = arrastamento de ar.
Instalar sempre válvulas de libertação de ar a jusante:
- Bombas
- Válvulas de controle
- Medidores de caudal
- Válvulas redutoras de pressão
Antes e depois das válvulas de isolamento
As válvulas de fecho rápido podem criar condições de vácuo.
Instalar válvulas de ar e vácuo em ambos os lados para evitar danos durante o funcionamento.
Como funcionam as válvulas de ar (a explicação simples)
Vou explicar a mecânica:
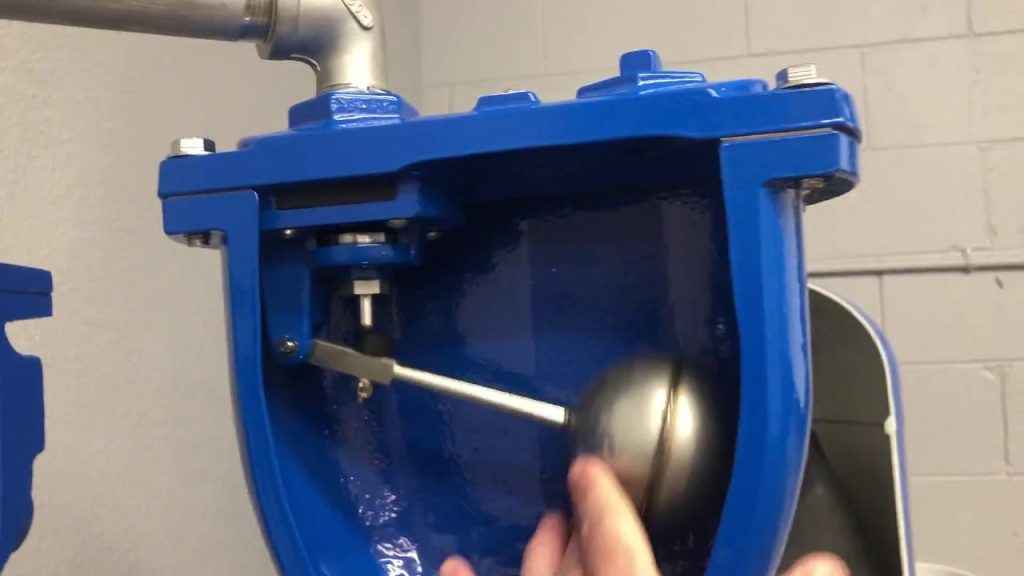
Para válvulas de libertação de ar:
- Acumulação de ar na câmara da válvula
- O flutuador desce porque o ar desloca a água
- Isto abre um pequeno orifício
- O ar escapa-se até a água voltar a subir
- A boia sobe e veda o orifício
Para válvulas de ar e vácuo:
- O flutuador grande mantém-se aberto quando o tubo está vazio
- A água sobe durante o enchimento, empurrando o ar para fora
- O flutuador sobe com o nível da água
- Fecha-se quando o tubo está cheio
- Abre novamente se a pressão descer abaixo da pressão atmosférica
Bastante simples, certo?
Mas eis o que a maioria das pessoas não vê:
O design do flutuador é crucial. As válvulas baratas utilizam flutuadores de plástico oco que podem ficar encharcados. As válvulas de qualidade utilizam flutuadores de aço inoxidável sólido ou de polímero projetado que duram décadas.
Problemas comuns das válvulas de ar (e como os resolver)
Mesmo as melhores válvulas de ar podem falhar.
Eis os problemas mais comuns que vejo:
Problema 1: A válvula não fecha
Sintomas: Pulverização contínua de água da válvula
Causas:
- Detritos que bloqueiam o selo
- Superfícies de vedação desgastadas
- Boia danificada
Fixar: Limpar ou substituir os componentes internos
Problema 2: A válvula não abre
Sintomas: Acumulação de ar apesar da presença da válvula
Causas:
- Orifício obstruído
- Boia encravada
- Tipo de válvula incorreto
Fixar: Desmontar e limpar, ou substituir pelo tipo de válvula correto
Problema 3: Golpe de aríete apesar das válvulas de ar
Sintomas: Ruídos de pancadas, picos de pressão
Causas:
- Fechamento demasiado rápido das válvulas
- Insuficiente válvula de ar capacidade
- Má colocação da válvula
Fixar: Instalar válvulas de fecho lento ou acrescentar mais válvula de ar capacidade
Dimensionamento de válvulas de ar (da forma correta)
É aqui que muitos engenheiros cometem erros.
As válvulas de ar são dimensionadas apenas com base no diâmetro da tubagem.
Grande erro.
O dimensionamento correto é considerado:
- Caudal: Caudais mais elevados necessitam de válvulas maiores
- Pressão de funcionamento: Afecta a capacidade de descarga de ar
- Perfil do gasoduto: Mais mudanças de altitude = mais tratamento de ar necessário
- Taxa de enchimento: Os sistemas de enchimento rápido necessitam de orifícios maiores
Utilize as tabelas de tamanhos do fabricante, mas lembre-se:
É melhor sobredimensionar ligeiramente do que subdimensionar. Uma válvula sobredimensionada continua a funcionar. Uma válvula subdimensionada causa problemas.
Melhores práticas de instalação
Quer que as suas válvulas de ar durem?
Siga estes conselhos de instalação:
Utilizar um suporte adequado
As válvulas de ar podem ser pesadas, especialmente os modelos maiores.
Nunca deixe que o peso da válvula exerça pressão sobre a tubagem. Utilizar bases de betão ou suportes de aço.
Instalar válvulas de isolamento
Instale sempre uma válvula de fecho por baixo de cada válvula de ar.
Isto permite-lhe prestar assistência ao válvula de ar sem drenar todo o sistema.
Considerar as câmaras de válvulas
Em climas gelados ou em áreas com muito tráfego, instalar válvulas de ar em câmaras de proteção.
Isto evita danos e facilita a manutenção.
Pensar na alta
As válvulas de ar podem descarregar água durante o funcionamento.
Encaminhar a descarga para longe de equipamento elétrico e de passagens. Já vi muitos riscos de escorregamento devido a uma colocação de válvulas mal planeada.
Manutenção que realmente importa
A maioria das válvulas de ar são bastante resistentes.
Mas não estão isentos de manutenção.
Eis o meu horário recomendado:
Mensal:
- Inspeção visual de fugas
- Verificar se as zonas de descarga estão desobstruídas
Anualmente:
- Válvulas de isolamento de exercício
- Limpar os componentes internos da válvula
- Verificar o funcionamento do flutuador
- Substituir os vedantes desgastados
De 5 em 5 anos:
- Reconstrução ou substituição completa
- Funcionamento da válvula de teste de pressão
Dica profissional: Tenha peças sobresselentes à mão. Quando uma válvula falha, é necessário repará-la rapidamente.
Considerações avançadas para 2025
O válvula de ar A indústria não está parada.
Eis o que há de novo:
Válvulas de ar inteligentes
Os novos modelos incluem sensores que monitorizam:
- Frequência de descarga de ar
- Ciclos de funcionamento da válvula
- Pressão interna
Estes dados ajudam a otimizar o desempenho do sistema e a prever as necessidades de manutenção.
Tecnologia Anti-Slam
As válvulas de elevado desempenho incluem agora caraterísticas que evitam o fecho por pressão, reduzindo martelo hidráulico risco.
Integração da proteção contra sobretensões
As válvulas combinadas modernas incluem frequentemente caraterísticas de antecipação de picos, proporcionando uma proteção adicional à tubagem.
O custo de errar
Deixem-me partilhar uma história rápida:
No ano passado, prestei consultoria a um sistema municipal de abastecimento de água que estava a sofrer repetidas falhas nas condutas.
O culpado? Inadequado válvula de ar cobertura.
A reparação custou $50.000 em válvulas de ar.
Mas poupou-lhes mais de $500.000 em reparações anuais de tubagens e perdas de água.
Trata-se de um retorno de 10 vezes só no primeiro ano.
O seu plano de ação
Pronto para otimizar o seu sistema?
Eis o que fazer:
- Auditoria das suas válvulas de ar actuais: Mapa das suas localizações e condições
- Identificar lacunas: Procurar pontos altos e trajectos longos sem válvulas
- Tamanho correto: Utilizar as ferramentas do fabricante e não a adivinhação
- Instalar estrategicamente: Seguir as diretrizes de colocação acima referidas
- Manutenção regular: Estabelecer um calendário de manutenção e cumpri-lo
A linha de fundo
O que é um válvula de ar?
É a apólice de seguro da sua conduta contra problemas relacionados com o ar. Desde a prevenção de golpes de aríete até à redução dos custos de energia, uma válvula de ar A seleção e a colocação de um produto rendem dividendos durante anos.
Não fique à espera que os problemas se desenvolvam. Obtenha o seu válvula de ar estratégia desde o início.
Os seus canos (e o seu orçamento) vão agradecer-lhe.