Ball valves, integral components in controlling the flow of fluids in numerous systems, serve as a critical point of interest for those involved in plumbing, HVAC, and various industrial applications. This article delves into the complexities and nuances of ball valves, beginning with a fundamental explanation of what a ball valve is, how it regulates fluid movement, and whether it is directional.
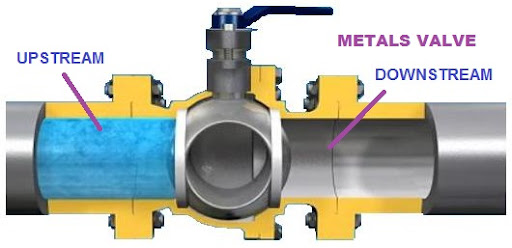
What is a Ball Valve and how does it work?
A ball valve is a type of valve that uses a spherical closure element to control the flow of fluid through a pipe or tube. It rotates the ball within the valve body to open or close the flow passage. This movement is controlled by the handle or actuator attached to the valve.
Types of Ball Valves
Ball valves come in various types, including floating, trunnion, and V-port ball valves. Each type has different construction and application features, allowing for versatility in flow control.
Operation of Ball Valves
Ball valves operate by rotating a ball with a bore to control the fluid flow. When the ball is in line with the pipe, the valve is open, and when it is perpendicular, the valve is closed, providing efficient flow control.
How ball valves control flow direction
Ball valves control flow direction by rotating a ball with a bore through it. The valve is open when the ball is in line with the pipe. When it is perpendicular, the valve is closed, providing efficient flow control.
Are ball valves directional?
Yes, ball valves can be either bidirectional or unidirectional. While most ball valves are bidirectional, V-ball valves are unidirectional and can only control flow in one direction. It is essential to determine the directionality of a ball valve for proper installation and optimal flow control.
Understanding flow patterns in ball valves
Understanding flow patterns in ball valves is crucial for efficient operation. The flow direction indicators on the valve body or handle and flow arrow markings on adjacent piping or equipment provide valuable information. By adhering to manufacturer instructions and examining valve markings, proper alignment can be ensured.
Factors Affecting Ball Valve Directionality
Factors affecting ball valve directionality include system requirements and the controlled fluid type. The system’s requirements will determine if an inherently directional ball valve is needed, while the type of fluid can also influence the directionality of the valve.
Design considerations for directional flow control
Design considerations for directional flow control include the orientation of the valve handle to ensure it opens in the direction of flow, as well as features like spring-loaded discs for added sealing and backflow prevention. These factors are crucial in selecting the correct ball valve for optimal performance and efficiency in fluid control systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ball valves can be directional or non-directional depending on their design and application. The orientation in which they are installed and the handle position determine the flow direction. It is essential to consider these factors when using ball valves in a system. A ball valve’s directionality refers to its ability to control fluid flow in a specific direction. While most valves are non-directional, ball valves can be directional or bi-directional, depending on their design and application.
Final thoughts on the directional nature of ball valves
Final thoughts on the directional nature of ball valves: Understanding the directionality of ball valves is crucial for proper installation and control of fluid flow. Whether non-directional or bi-directional, ball valves play a significant role in various industries and applications. Proper design considerations and knowledge of flow patterns ensure optimal performance.