What are we talking about when we talk valve connections? Today’s topic is about some common valve connection types, including flange (RF, FF, RTJ), Screw (NPT, BSPT), Weld (Butt Weld, Socket Weld), and some codes and standards for these connections.
Valve Connection Type
Flange Connection
Flange connection type is the easiest connection to be installed or uninstalled from a pipeline. Arguably these are the most commonly used end connections at present.
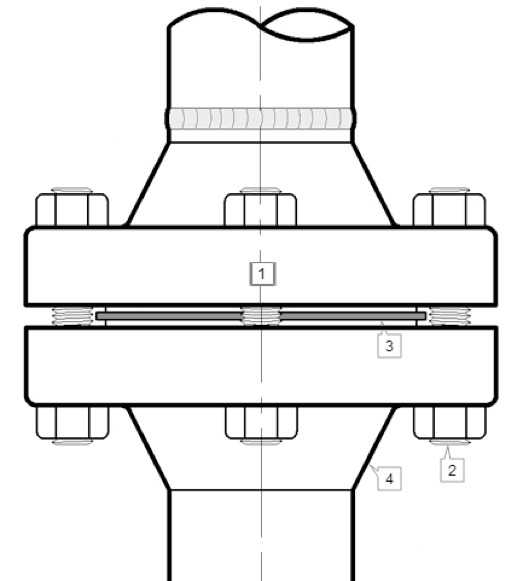
Raised Face Flange – RF
The most common type used in process plant applications are the Raised Face flanges. This flange is preferred because of its raised gasket surfaces above the bolting circle face. This design allows the use of a wide combination of gasket designs, including flat ring sheet types and metallic composites such as spiral wound and double jacketed types.
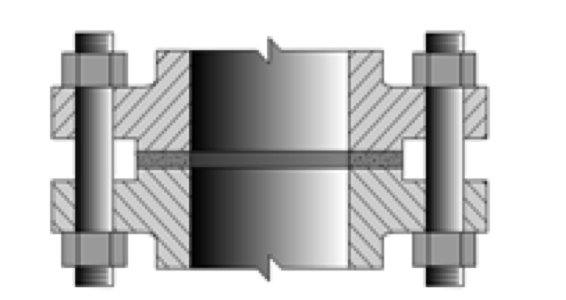
Flat Face Flange – FF
The Flat Face – FF flange has a gasket surface that is in the same plane as the bolting circle face. Applications using flat face flanges are frequently those in which the mating flange or flanged fitting is made from a casting (e.g. bronze and iron valves). Additionally, according to ASME B31.1, when connecting flat face cast iron flanges to carbon steel flanges, the raised face on the carbon steel flange must be removed, and a full face gasket is required.
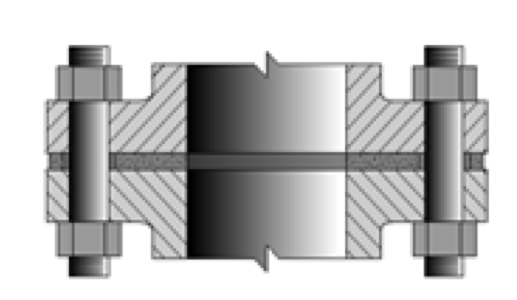
Ring-Type Joint Flange – RTJ
A Ring-Type Joint can also have a raised gasket face with the difference being the ring groove machined in this face. This groove will accommodate a steel ring gasket for flange mating
Screw Connection
Threaded connections are very common. They provide a compact and streamlined connection between the valve and pipe.
NPT – National Pipe Taper Threads
This is a U.S. standard for tapered threads used on threaded pipes and fittings. In contrast to straight threads like those that are found on a bolt, a taper thread will pull tight and therefore make a fluid-tight seal. Pipe tape or pipe compound should be used on the threads to ensure a fluid-tight seal.
BSPT – British Standard Pipe Taper Threads
This standard is similar to NPT, where the threaded portions of the connection are tapered. The only difference is the angle of the thread flanks. The angle from root to crest on BSPT threads is 55° as opposed to 60° for NPT. It is possible for a male NPT to fit into a female BSPT, but due to the difference in the thread angle, a fluid-tight seal will not be made.
BSPP – British Standard Parallel Pipe Threads
This type of thread does NOT form a fluid-tight seal as the tapered threads do. The use of a soft seal is required to do so. These threads will pull the 2 mating parts together, and compress the soft seal between flat surfaces on each component.
Welded End Connection
Welded connections are used where zero leakage is important to the system. This is typically in high-temperature and high-pressure piping systems. It is also common to use welded connections with chemically dangerous fluids. Trained professionals should carry out welded connections. They are a permanent type of connection. There are two main types of welded connections for valves:
Socket Welded Connections
This type of welded connection has a valve diameter larger than the pipe’s diameter, such that the pipe can fit into the valve socket end. The weld is done around the rim of the valve end that is connected to the pipe.
Butt-Welded Connections
In this welded connection, the valve ends and the pipe ends have the same diameter. The connection ends are placed against each other and grooved to create a space for the weld. The weld is done around the rims of the connection. Butt welding is common for smaller pipe sizes.
Classification of Flanges

The new standard flange connection is an important connection for pipeline construction. Using bolts to connect two pipelines, fittings or equipment together is called flange connection, also between these two flanges, you need to add flange gaskets to fasten the connection. Some fittings and equipment which already have flange plates themselves also belong to flange connection.
The new standard flange can be divided into a screw connection flange and welded flange. Low pressure and small diameter situation is suitable for wire flange while welded flange is more often used in high/low pressure and large diameter situation. Flanges with different pressure will have different thicknesses, as well as the diameter and quantity of connecting bolts. Depending on the level of pressure, flange gaskets will also have various materials, such as low-pressure asbestos gaskets, high-pressure asbestos gaskets, metal gaskets, and so on. Available to withstand great pressure, flange connection is easy to use.
The new standard flange connection has a wide application in the industrial pipeline. Within the family, it is not possible to see the flange connection because of the small pipe diameter and low pressure. But if you are in a boiler room or production site, flanged pipes and equipment will be scattered everywhere.
Related Tags :
Ten articles before and after
Distinguish Electric Knife Gate Valve – News – Zeco Valve | API Butterfly Valve supplier
Application & Installation of High Pressure Control Valve – Zeco Valve | Quality valve supplier
Three Types of Valve Connection – Zeco Valve | Quality valve supplier
Material and Application of Stainless Steel Flanges – Zeco Valve | Quality valve supplier
What Is The Assembly Workflow Of The Check Valve? – News – Zeco Valve | API Butterfly Valve supplier
The Composition of Spring Micro Open Safety Valve – Zeco Valve | Quality valve supplier