Use ball valves to reliably and effectively manage the flow of liquid or gas in a piping system. The difference between full and standard port ball valves is a crucial one among the various ball valves that are available. In this blog post, we will discuss what a full port ball valve is and its benefits over a normal one.
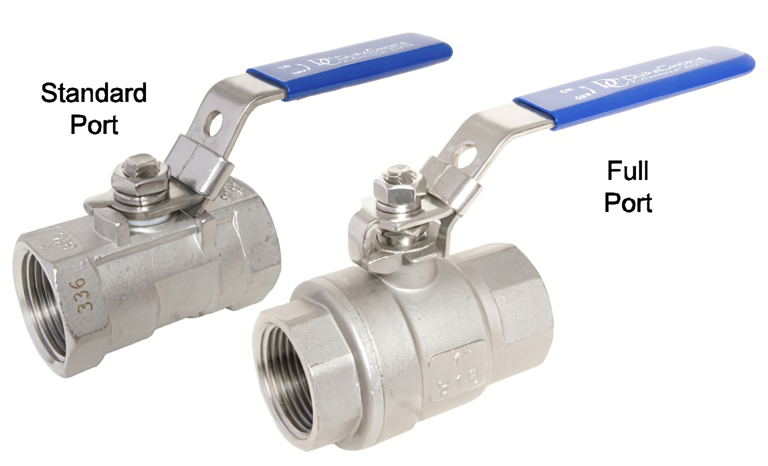

What is a full port ball valve?
Full port or full bore ball valves provide a direct flow route with no reduction in liquid flow. The pipe or tube at the valve’s inlet and outlet has the same diameter as the ball valve’s interior, allowing maximum fluid flow and a minimal pressure drop. Due to its design, it is the perfect option for applications that call for high flow rates, low-pressure dips, and little turbulence.
Due to its direct flow channel, the valve is simple to clean and maintain. Pipelines, water treatment facilities, and chemical processing businesses are where it is most frequently employed. Full port ball valves are a dependable, economical method of controlling fluid flow.
The full port meaning of the full port ball valve
“Full port” in the context of ball valves refers to a design element that permits unhindered fluid passage when the valve opens. A full port ball valve, often called a full-bore ball valve, is distinguished by having an aperture or bore the same diameter as the attached pipeline. This guarantees that the flow rate won’t significantly decrease as the fluid passes through.
When compared to their counterparts with conventional ports, these valves are often bigger. To accommodate the complete, unrestricted flow, the design includes a larger ball and a larger hole or “port.” A full port ball valve effectively continues the pipeline when fully opened, ensuring minimum pressure drop and unrestricted flow.
How a Full Port Ball Valve Works?
As Wikipedia explains, a full port ball valve is distinct because of its oversized ball and bore. Due to the larger diameter, the valve doesn’t reduce the flow of the substance passing through. This design makes these valves ideal for situations where the flow rate is a major concern.
The internal mechanism and components of the full port ball valve
- The valve’s body houses the ball, which rotates on its axis.
- The ball has a hole, or port, which allows flow when the valve is opened.
- Seal seats facilitate sealing, ensuring no leakage occurs when the valve is closed.
The rotation of the ball, which can be manually controlled or automated, is the mechanism that either opens or closes the valve. The full port design ensures minimal resistance to flow when the valve is open.
Step-by-step process of opening and closing the valve
- When the handle aligns with the valve, the valve is completely opened. The ball’s hole aligns with the flow direction, allowing passage.
- The valve is closed by turning the handle 90 degrees perpendicular to the valve. The ball rotates, blocking the flow.
Essentially, the operation of a full port ball valve is as straightforward as “quarter-turn equals open or closed.”
What are the advantages of a full port valve?
Advantages of a Full Port Valve
- Versatility: Full port valves are incredibly versatile. They can be effectively employed in various industries, including oil and gas, food processing, etc. This is because they can handle a variety of materials, including gases, liquids, steam, and slurries.
- Excellent Flow Characteristics: Full port valves have superb flow characteristics as they possess larger internal diameters than other valves. This larger diameter enables unrestricted flow through the valve, causing a minimal pressure drop. Such properties make full port valves ideal for applications necessitating high fluid flow rates.
- Quick Response Time: Full port valves can be opened or closed quickly, often with just a quarter-turn. This makes them perfect for instances requiring swift response times.
- Reliability and Maintenance: Full port valves are reliable and sturdy. They require minimal maintenance over their lifespan, as they are designed to last longer than other valves without compromising performance or efficiency.
- Cost Consideration: Despite being larger, full port valves are still relatively inexpensive compared to other valves available on the market. This makes them a cost-effective solution in many industrial applications.
Applications of Full Port Ball Valves
Full port ball valves find extensive use in several industries due to their flow efficiency and their resistance to cavitation. Known for their wide opening, full port ball valves don’t restrict the flow of liquids or gases passing through, making them perfect for applications that require a steady, high-volume flow.
Industries where full port ball valves are commonly used
Oil and Gas Industry: Full port ball valves effectively control the flow of natural gas or crude oil.
Chemical Industry: Given their damage-resistant design, these valves are perfect for transporting corrosive substances.
Specific use cases and examples
Water Supply Systems: These valves are used in residential and commercial water systems because of their high efficiency. [source]
Industrial Machinery: High-volume hydraulic and pneumatic systems use full port ball valves for effective flow control.
Food and Beverage Industry: Full port ball valves help maintain hygiene standards while allowing high-volume flow in this industry.
Pharmaceuticals: These valves are used in delicate drug manufacturing processes.
Remember, the main consideration for selecting a full port ball valve is if the application requires a steady, high-volume flow without pressure drops.
How to Choose the Right Full-Port Ball Valve
Selecting the right full port ball valve comes down to understanding your flow needs. A full port valve is ideal for situations where minimum resistance to flow is required.
Factors to consider when selecting a valve
- Intended use: Full port valves are excellent for shutoff and control applications but unsuitable for fine flow control or throttling.
Guidelines for proper sizing and compatibility
- Size: Ensure the valve’s diameter matches the pipe’s inner diameter. This ensures an unobstructed flow path.
- Material compatibility: Consider the material of your valve – brass, stainless steel, or plastic – according to your temperature and pressure requirements.
What is the difference between standard port and full port ball valves?
A standard port and a full port ball valve primarily differ in the diameter or size of the bore (openings) through which the medium flow passes about the pipeline that serves as a valve.
Full Port Ball Valve
These are valves where the bore size is identical to the flow path. This means the flow pressure doesn’t change as it passes through the valve, and no flow resistance is observed. Full port ball valves are ideal for pipes carrying liquids and solids due to their unrestricted nature. However, they are more expensive and may require more space than standard port ball valves.
Standard Port Ball Valve
On the other hand, a standard port ball valve has a smaller diameter than the connecting pipeline, typically about 75%-90% of the original size. This leads to a reduction in flow pressure and increases the risk of cavitation. Although they cost less and take up less space than a full port ball valve, they may not be the best option for applications where maintaining consistent flow pressure is necessary.
In conclusion
Ball valves aid in regulating the liquid or gas flow through pipelines. Ball valves come in two varieties: full port and regular port. Ball valves with full ports allow liquid to pass through without slowing down. They work well in locations that require high flow rates with minimal pressure drop. They are simple to maintain and clean. They are frequently employed in the pipeline, water treatment, and chemical processing sectors. They are a tad larger than ball valves with conventional ports. However, standard port valves have a smaller opening, which lowers the flow rate. They might be less expensive and smaller than full port ball valves, but they might not be ideal for ensuring constant flow.