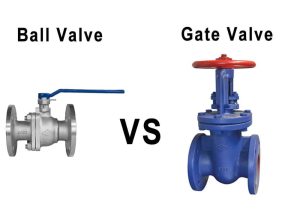
Valves regulate and control flow and pressure in pumping systems. They also play an important role in site safety. Understanding the types of valves and how they work can help end users select the right valves for their application’s use.
What is a Pump Valve?
A pump control valve automatically regulates the pump start-up and shut-down in a time-controlled to minimize system hydraulic surges. The pump control valve is electrically interfaced with the pump motor, the Pump Control Valve “opens” and “closes” at an adjustable speed, providing a smooth, predictable transition of pump discharge flow into the system. Several options are available including “Check Feature” preventing backflow.
Which Valve is used in Pump?
A pumping system typically requires three valves: an inlet (suction) shut-off valve, an outlet (discharge) shut-off valve, and a check valve between the pump discharge nozzle and the discharge shut-off valve to avoid reverse flow and protect the pump from back pressure.
Occasionally, a foot valve can be installed on the inlet pipe to maintain pump prime or to protect it from reverse rotation. However, potential drawbacks to foot valves such as impacts to net positive suction head available and risk of water hammer (a pressure surge caused by an abrupt change in the pump rate of flow) must be considered.
Note that some systems will not require these valves, and some will require additional valves for isolation and control. Specification and application for these valves and control valves can be referenced in ANSI/HI 9.6.6 Rotodynamic Pumps for Pump Piping, and HI’s “Pump System Optimization: A Guide for Improved Energy Efficiency, Reliability, and Profitability.”
Sometimes, the discharge isolation valve and the check valve can be replaced by a triple-duty valve, which provides both isolation and backflow prevention in one piece. They can also provide circuit balance.
Where to Put a Valve on the Pump
Valves on a pump control the flow of liquid through a pump. These help to regulate pressure within a pump and prevent possible breakage. Any pump should have two valves attached; one at the inlet, or suction, and the other at the outlet, or discharge area.
Valves must be installed at the correct distance in order to ensure maintenance and safety. This can be determined by using the width of each valve as a measure. For example, if a pump has a 1-inch inlet and ½-inch outlet, then a valve should be placed a minimum of 10 inches from the suction side and 5 inches away from the discharge.
The valve on the suction side should only be closed when the pump is turned off. Upon startup, the valve on the outlet should not be fully open, it should be partially closed to generate some extra back pressure.
Related Tags :
Ten articles before and after
Use Of Globe Valve – News – Zeco Valve Co.,Ltd | API 6D ball valve manufacturer
Introduction To Needle Valve – News – Zeco Valve Co.,Ltd | API 6D ball valve manufacturer
Preventive Measures For Valve Failure – News – Zeco Valve Co.,Ltd | API 6D ball valve manufacturer
Classification Of Check Valves – News – Zeco Valve Co.,Ltd | API 6D ball valve manufacturer
Check Valve Maintenance And Maintenance – News – Zeco Valve Co.,Ltd | API 6D ball valve manufacturer