Flange gaskets work like other gaskets by sealing the surface on which they are used. They are known as “flange gaskets,” however, because they are intended for use on a flanged surface.
What is a flange gasket?
Flange gaskets are designed to seal the space between two sections of pipe. Most pipes, of course, are joined at a flanged surface. The surface where two pipes join isn’t smooth or otherwise flat. Rather, it’s flanged, meaning it flares out. For flanged surfaces such as this, flange gaskets are used.
How Flange Gaskets Work
Flange gaskets work in the same way as most other gaskets. When installed, they create a sealed mating surface so that water or other liquids won’t leak out. Pipes typically have water or liquids flowing through them. If two pipes are joined together, the water or liquids may leak out through this mating surface. Flange gaskets prevent this from happening by sealing the surface.
Pipes generally don’t offer a sealed mating surface when used alone. This is especially true in the case of pipes with a flanged surface. Since flanged surfaces are flared, water and liquids can easily escape through the cracks. A simple solution to prevent leaks is to install a flanged gasket. The flanked gasket will contour to the shape of the pipes’ flanged surface so that water or liquids stay within the pipes.
Types of Gaskets
Non-Metallic Flange Gaskets (Rubber Flange Gasket)
These are usually composite sheet materials are used with flat-face and raised-face flanges in low Pressure Class applications. Non-metallic gaskets are manufactured from arimid fiber, glass fiber, elastomer, Teflon® (PTFE), graphite etc.. Full-face gasket types are suitable for use with flat-face flanges. Flat-ring gasket types are suitable for use with raised face flanges.
Introduction of PTFE gasket
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) packing gasket is a kind of non-metallic composite cushion, which is generally composed of two parts: the cover and the insert. The main function of the envelope is anti-corrosion, which is usually made of polytetrafluoroethylene. The insert (filler) is a non-metallic material with or without metal reinforcement, which is usually made of asbestos rubber sheet.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) packing gasket is mainly suitable for full plane and raised face steel pipe flange connection. It is suitable for corrosive medium with nominal pressure PN of 0.6 ~ 5.0mpa and working temperature of 0 ~ 150 ℃ or medium with high cleanliness requirements.

Form of PTFE gasket
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gasket for pipe flange can be divided into three types according to manufacturing methods: cutting type (s type), machining type (M type) and folding type (F type).
For the machined packing gasket, the inner diameter of the packing layer can be consistent with the inner diameter of the flange, so as to prevent the eddy current of the fluid at the flange. As for the folded packing gasket, it is made of 0.4-0.8 mm thick polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) film. After heat sealing, both ends of the gasket are wrapped outside the annular core material in U shape. It is easy to manufacture and suitable for large flange sealing.
Semi-Metallic Gaskets
These are composites of metal and non-metallic materials. The metal is intended to offer strength and resiliency, while the non-metallic portion provides conformability and sealability. Often used semi-metallic gaskets are spiral wound and camprofile, and a variety of metal-reinforced graphite gaskets.
Semi-metallic are designed for almost all operating conditions and high-temperature and pressure applications, and are used on raised face, male-and-female, and tongue-and-groove flanges.
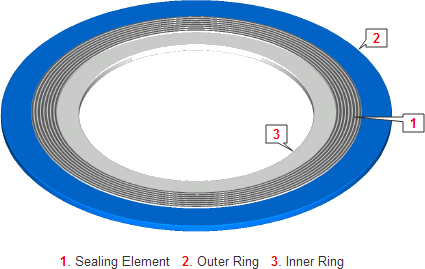
Metallic Gaskets
These are fabricated from one or a combination of metals to the desired shape and size. Often used metallic gaskets are ring-type-joint gaskets (RTJ). They are always applied to special, accompanying flanges which ensure good, reliable sealing with the correct choice of profiles and material.
Ring Type Joint gaskets are designed to seal by “initial line contact” or wedging action between the mating flange and the gasket. By applying pressure on the seal interface through bolt force, the “softer” metal of the gasket flows into the microfine structure of the harder flange material, and creating a very tight and efficient seal.
Related Tags :
Ten articles before and after
A890 4A Dual Plate Wafer Check Valve – News – Zeco Valve | Professional valve manufacturer
News – Common materials of valve stem | API 609 Butterfly valve manufacturer
News – Wafer-Style Butterfly Valve | API 609 Butterfly valve manufacturer
News – Structural characteristics of butterfly valve | API 609 Butterfly valve manufacturer
News – Flange gasket (1) | API 609 Butterfly valve manufacturer
News – Advantages and disadvantages of butterfly valve | API 609 Butterfly valve manufacturer
Titanium Alloy Valves – News – Zeco Valve | Professional valve manufacturer
News – Inspected by SGS inspect factory- Fortis Valve | API 609 Butterfly valve manufacturer
The Criteria And Types Of Chemical Valves – News – Zeco Valve | Professional valve manufacturer