Heat exchangers are devices designed to transfer heat between two or more fluids—i.e., liquids, vapors, or gases—of different temperatures. Depending on the type of heat exchanger employed, the heat transferring process can be gas-to-gas, liquid-to-gas, or liquid-to-liquid and occur through a solid separator, which prevents mixing of the fluids, or direct fluid contact.
Types of Heat Exchangers
Based on the design characteristics indicated above, there are several different variants of heat exchangers available. Some of the more common variants employed throughout industry include:
Spiral Heat Exchanger
Spiral heat exchangers are circular units containing two concentric spiral flow channels, one for each fluid. The different media flow counter currently: one fluid enters the centre of the unit and flows towards the periphery, the other enters the unit at the periphery and moves towards the centre. The channels are curved and have a uniform cross section. There is no risk of intermixing.
The product channel is normally open on one side and closed on the other. The channel for the heating/cooling medium can sometimes be closed on both sides, depending on the cleanliness of the heating/cooling medium. Each channel has one connection in the centre and one on the periphery of the heat exchanger.
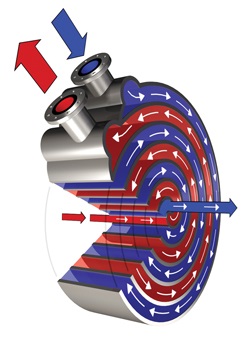
Why do we use spiral heat exchanger?
- Handle crossing-temperature condition in a single spiral
The fully countercurrent system(KSH-1) is able to exchange heat even if temperature difference is extremely close.
- Long time operation is possible
Spiral heat exchanger is very good at using with fluids that tend to cause fouling. Single channel geometry reduce the fouling, and it called “self-cleaning”. Self-cleaning means that when fouling occur in spiral channel, taking it away from. Because the entire flow have to pass through fouling section. It means that velocity of fouling-section increase. So scrubbing effect will happen.
- High Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient
Spiral heat exchanger flow passage easily creates turbulent flow. Optimum flow speed can be gained by selecting the most suitable spiral channel. High Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient can be achieved.
- Less maintenance
Generally, when install the spiral type, to cut down maintenance cost. Compare that with any other heat exchanger
- Space Saving
SHE equipment volume is far compact comparing to Tubeler Heat Exchanger. Plant space can be saved and plant initial cost can be saved.
Tubular heat exchanger
A tubular heat exchanger (THE) is used to warm or cool a product by exchanging heat between the process fluid and a service fluid, which is typically water, ice water, glycol or steam. The hot or cold service fluid flows around the tubes within the THE and heat is transferred between the product and the media.
The rate of heat transfer is dependent on the tubular heat exchanger configuration, temperature differential, size of tubes, turbulence in the flow and flow velocity. Different configurations are available, and the selection of the best solution is based on the properties of the process fluid and production goals. Our experience and expertise will help ensure you receive the best solution for your specific needs in terms of production goals, costs, efficiency and product quality.
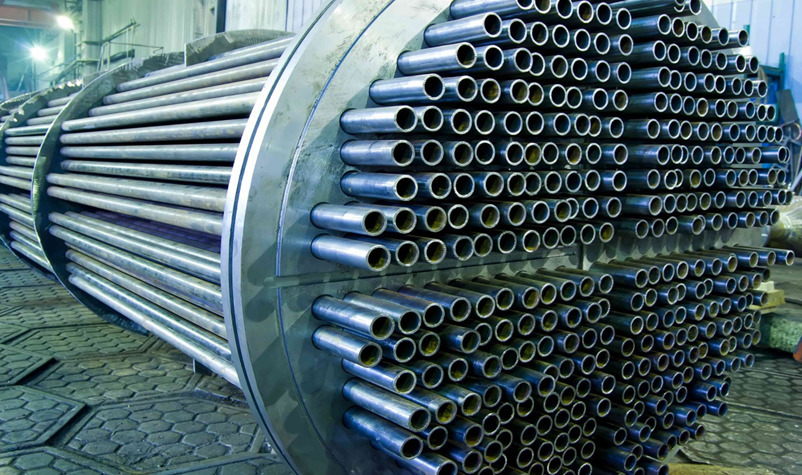

Where are tubular heat exchanger used?
The tubular heat exchanger is a process equipment used in different industries, and its applications are very diverse and varied. The advantages of tubular heat exchangers make them very robust, reliable and low maintenance equipment, due to the absence of joints.
- Sanitary applications: Applications destined for the Food Industry with optimized designs to favor a good CIP cleaning (Clean in Place) of the product channel, guaranteeing the best finishes and the drainability.
- Pharmaceutical applications: Applications destined for the Pharmaceutical Industry, in which the roughness certification plays a key role, and whose design is specially designed to avoid cross contamination
- Industrial applications: Applications destined for the Chemical and Petrochemical Industry (Oil and Gas), whereby high priority has been given to ensure long life and high reliability.
Advantages of Tubular Heat Exchangers
Within the different geometries of heat exchangers present in the market as plate and gaskets, welded plates, spiral or scraped surface heat exchangers, among others, the tubular geometry is one of the most traditionally used.
The main advantages of tubular heat exchangers are as follow:
- Low maintenance cost
- High working pressure
- High working temperature
- Processing of particulate or fibre products
- Easy inspection and disassembly
- High security in aseptic processes
- Easy to enlarge
Double pipe heat exchanger
A double-pipe heat transfer exchanger consists of one or more pipes placed concentrically inside another pipe of a larger diameter with appropriate fittings to direct the flow from one section to the next. One fluid flows through the inner pipe (tube side), and the other flows through the annular space (annulus). The inner pipe is connected by U-shaped return bends enclosed in a return-bend housing. A typical double-pipe heat transfer exchanger is shown in Fig. 1. Double-pipe heat exchangers can be arranged in various series and parallel arrangements to meet pressure drop. The major use of the double-pipe heat exchanger is the sensible heating or cooling process of fluids where small heat transfer areas (up to 50 m2) are required. This configuration is also very suitable for one or both of the fluids at high pressure because of the smaller diameter of the pipes. The major disadvantage is that they are bulky and expensive per unit of heat transfer surface area.
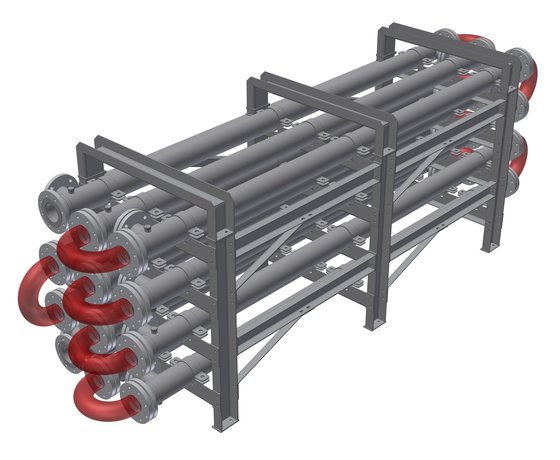

Where we use the double pipe heat exchanger?
It is hard to encompass all of the applications for double pipe heat exchangers. To name just a few, they are popular in high pressure and temperature applications such as boilers and compressors, as well as sensible heating and cooling in process engineering systems. They are found in fields ranging from petroleum refining to refrigeration to sewage treatment to space heating, so it is clear that the possibilities are endless with such a useful, elegant design. If space is at a premium and simplicity is paramount, consider a double pipe heat exchanger for the job.
What are the advantages of double pipe heat exchanger?
The double pipe heat exchanger is one of the easiest designs to fabricate, add on to, and repair thanks to its simple design. They have some unique advantages over some of the more complicated heat exchanger designs, as well as some important disadvantages, so this article will show buyers when they should – and shouldn’t – consider using one of these systems:
Below is a list of the main advantages of using a double pipe heat exchanger:
- They can handle both high pressures and high temperatures well
- Their parts have been standardized due to their popularity, allowing for easy part sourcing and repair
- They are one of the most flexible designs, allowing for easy addition/removal of parts
- They have a small footprint that requires little to no maintenance space while still having good heat transfer
It is important to understand the downsides of such a design, however, which include:
- They are limited to lower heat duties than other, larger designs
- Even though they are able to be used in parallel flow, they are more often only used in counterflow regimes, which restricts some applications
- Leaking can occur, especially when paired with more units
- The tubes are easily fouled and difficult to clean without disassembling the whole heat exchanger
- If the budget and space exists for a shell and tube exchanger, then a double pipe design is often a less efficient method of heat transfer
For more information about Heat Exchangers, contact Zeco Valve. Email them at commercial@zecovalve.com or visit https://www.zecovalve.com.
Related Tags :
Ten articles before and after
Providing Pipeline Valves in the Mountain West, Southwest, and Front Range Regions | Zeco Valve Blog
BS&B FlameSaf Arrester Products | Zeco Valve Blog
The MASCOT GFlo Globe Control Valve | Zeco Valve Blog
Zeco Valve Industrial Control Valves from Zeco Valve | Zeco Valve Blog
CCS Pressure Switches for Oil, Gas and Pipeline Applications | Zeco Valve Blog
Drop-in Replacement Heat Exchangers and Tube Bundles That You Save Time and Money | Zeco Valve Blog
Buckling Pin Pressure Relief Devices | Zeco Valve Blog
AMETEK FPP XXP280 High Purity Heat Exchangers | Zeco Valve Blog