What is an Orbit valve?
Orbit valve is a type of ball valve. The orbit valve employs a tilt-and-turn mechanism that eliminates seal rubbing. Seal rubbing is the main cause of failure in valves such as ball valves, gate valves, and plug valves. These valves have strong seals mostly made of metal to enhance their ability to work in challenging and aggressive conditions. Orbit valves are suitable for use in meter isolation, flow lines, bypass and block, dryer switching, emergency shutdown, product segregation, discharge, and suction isolation among others. Orbit valves are used in several industries such as gas, oil, petrochemical, and other industries.

Who Makes Orbit Valves?
Only a few years after Oklahoma gained statehood in 1907, an individual by the name of Alfred “Alf” Heggem founded The Oil Well Improvements Company of Tulsa, an iron factory and machine shop. The Oil Well Improvement Company of Oil manufactured and sold oil well supplies and machinery. While Heggem innovated many product ideas in the valve world, his groundbreaking ball valve seating principle was considered to be the first major advancement for valves in over a fifty-year period. He patented his idea in 1935, and almost 85 years later, it is still the forerunner to ball valves today. The same engineering technology still safeguards against seat rubbing, which is a leading factor for why the ORBIT valve is world-renowned for its high integrity and its long service life.
Is an Orbit Valve a Ball Valve or?
An Orbit valve is a type of ball valve. Specifically, it is a trunnion-mounted ball valve, which means that the ball is supported by trunnions or shafts that are connected to the valve body. This design allows for greater stability and strength, which is particularly important for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
The name “Orbit valve” is a trademarked name used by the Cameron company for their line of trunnion-mounted ball valves. These valves are widely used in the oil and gas industry, as well as in other industries that require reliable and high-performance valves for demanding applications.
In summary, an Orbit valve is a type of ball valve, but one that is specifically designed with trunnions to provide greater strength and stability in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Operating Principle of Orbit Valves
Every Orbit valve incorporates a proven tilt and turn operation that eliminates seal rubbing, which is the primary cause of valve failure. When an Orbit valve is closed, the core is mechanically wedged tightly against the seat, assuring positive shut-off. When an ORBIT valve begins to open, the core tilts away from the seat, and line flow passes uniformly around the core face. This eliminates the localized high-velocity flow that typically creates uneven seat wear in ordinary ball, gate, and plug valves. The core then rotates to the fully open position.
The absence of seal rubbing during both opening and closing means easy, low-torque valve operation and long-term reliable performance. When valve leakage cannot be tolerated, the ORBIT operating principle can be relied upon to deliver a positive shut-off.
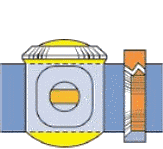
- To close an ORBIT valve, as the handwheel is turned, the stem begins to lower.
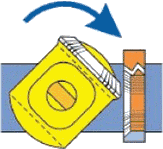
2. Precision spiral grooves in the stem act against fixed guide pins, causing the stem and core to rotate.
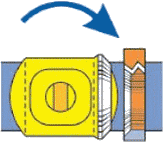
3. Continued turning off the handwheel rotates the core and stem a full 90° without the core touching the seat.
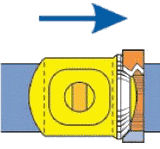
4. Final turns of the handwheel mechanically wedge the stem down, pressing the core firmly against the seat.
Applications of Orbit Valves
Orbit valves, which are a type of trunnion-mounted ball valve, are commonly used in a variety of applications across a range of industries. Some of the most common applications of Orbit valves include:
- Oil and gas production: Orbit valves are commonly used in oil and gas production facilities, particularly in upstream applications such as wellhead control, manifold systems, and pipeline pigging operations. The valves are well-suited to these applications because they can withstand high pressures and temperatures, and provide reliable shut-off and control of fluid flow.
- Refining and petrochemical processing: Orbit valves are also commonly used in refineries and petrochemical processing plants, where they are used for various processes such as distillation, cracking, and fractionation. The valves are often used in high-temperature and high-pressure applications and are capable of handling a range of corrosive and erosive fluids.
- Power generation: Orbit valves are used in power generation plants, where they are used to control the flow of steam and other fluids in boilers and other equipment. The valves are well-suited to these applications because they can handle high temperatures and pressures, and provide reliable control over the fluid flow.
- Water treatment: Orbit valves are also used in water treatment facilities, where they are used to control the flow of water and other fluids in various stages of the treatment process. The valves are often used in high-pressure applications and can handle a range of corrosive and abrasive fluids.
Overall, Orbit valves are a versatile and reliable type of ball valve that can be used in a variety of demanding applications across a range of industries. They are well-suited to applications that require high-pressure and high-temperature capabilities, as well as those that involve corrosive or erosive fluids.
Structural Features of Orbit Valves
- No Rubbing Between Sealing Surfaces
- The tilt-and-turn action eliminates seal abrasion, which is the major cause of seat wear in the conventional ball, gate, and plug valves
- Injectable Packing
- For in-service maintenance, stem packing material is injected through the packing fitting, giving complete control of fugitive emissions. (Available on all enclosed bonnet models.)
- Single-seat Design
- The single, stationary seat in the Orbit valve seals in both directions and avoids the problems of trapped pressure between seals.
- Long Life
- Orbit valves replace troublesome ball valves, gate valves, globe valves, and plug valves. The ORBIT design has performance advantages that reduce plant outages and reduce the cost of ownership.
- Optimum Flow
- Full port or reduced port openings give high CV figures. System pumping efficiency is enhanced and erosion problems are reduced.
- Top-entry Design
- In-line inspection and repair, after system depressurizing, simplifies maintenance.
- Dual Stem Guides
- Hardened stem slots and tough guide pins control the lift-and-turn action of the stem.
- Self-cleaning
- Tilting the core away from the seat before rotation causes immediate flow around 360 degrees of the core face. Product flow flushes any foreign material away from the seat without localized, high-velocity erosive flow.
- Low-torque Operation
- Orbit valves turn easily because seal rubbing is eliminated.
- Wear-resistant Hard\
- Facing on Core The core face is a hard, polished material that will endure difficult service, without loss of sealing integrity.
- Mechanical Cam Closure
- The cam angle at the lower end of the stem provides a mechanically energized seal
Why is my Orbit Valve Leaking?
If your Orbit valve is leaking, there could be several possible causes. Here are some of the most common reasons why a trunnion-mounted ball valve like an Orbit valve may experience leakage:
- Damage to the valve seats: The valve seats are the parts of the valve that provide a seal around the ball. If the valve seats become damaged or worn, they may no longer provide a tight seal, which can cause leakage. This can be caused by various factors, such as debris or corrosion.
- Problems with the valve stem: The valve stem is part of the valve that connects the actuator to the ball. If the stem is damaged or worn, it may not be able to properly control the movement of the ball, which can cause leakage. This can be caused by issues such as corrosion or improper installation.
- Damage to the ball: The ball is the main part of the valve that controls the flow of fluid. If the ball becomes damaged or warped, it may not be able to properly seal against the valve seats, which can cause leakage. This can be caused by factors such as corrosion or wear and tear.
- Problems with the valve actuator: The valve actuator is part of the valve that controls the opening and closing of the valve. If the actuator is malfunctioning or damaged, it may not be able to properly control the movement of the ball, which can cause leakage.
- Improper installation: If the valve was not installed correctly, it may not be able to properly seal against the pipeline or other components, which can cause leakage.
To determine the exact cause of the leakage, it is important to have a qualified technician perform a thorough inspection of the valve. Based on their findings, they can recommend the appropriate repairs or replacement parts to fix the issue and prevent future leakage.
How to Repair Orbit Valves?
If your Orbit valve is experiencing issues or damage, it may require repair in order to restore proper function. Here are some steps for repairing an Orbit valve:
- Diagnose the problem: The first step in repairing an Orbit valve is to diagnose the problem. This may involve inspecting the valve for damage or leaks and determining the root cause of the issue.
- Disassemble the valve: Once the problem has been identified, the valve will need to be disassembled in order to access the damaged or worn components. This will typically involve removing the actuator, stem, and ball.
- Inspect the components: With the valve disassembled, each component should be inspected for damage or wear. Common issues that may require repair or replacement include damaged valve seats, worn stem packing, or a damaged ball.
- Repair or replace damaged components: Once the damaged components have been identified, they should be repaired or replaced as necessary. This may involve replacing the valve seats, repacking the stem, or replacing the ball.
- Reassemble the valve: Once the damaged components have been repaired or replaced, the valve can be reassembled. This will typically involve reinstalling the ball, stem, and actuator, and reattaching any other components that were removed during the repair process.
- Test the valve: Once the valve has been reassembled, it should be tested to ensure that it is functioning properly. This may involve pressure testing the valve or performing a leak test to ensure that there are no leaks.
- Reinstall the valve: Once the valve has been repaired and tested, it can be reinstalled in the pipeline or equipment where it is needed.
It is important to note that repairing an Orbit valve can be a complex and technical process, and it is typically best to have a qualified technician perform the repair work. This can help ensure that the valve is repaired properly and that it will function reliably over the long term.
What is an Orbit Ball Valve?
The orbit ball valve is also called the bevel gear drive the warlords, suitable for aviation kerosene, crude oil, light oil, natural gas, liquefied gas, gas pipelines, and chemical medium pipelines, as an ideal device for truncated medium. Double off and working principle of the key drainage function of the valve is two pieces of sealing slide action installed in the plug.
This product is close to the gate, and with the flange connection, the Orbit Ball Valve body adopts the principle of rotation to achieve opening and closing. Reasonable design, simple and beautiful, to meet the market demand. Suitable for pressure levels 150~900Lb (1.6~32.0MPa), pipeline various working temperatures of -29~150 ℃ petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, chemical, electric power industry, and so on, cut off or connected to the pipeline medium.

Working principle of Orbit Ball Valve
State orbit ball valve fully open, the valve plug aligned channel, and the minimum pressure drop can guarantee the ideal. Turn the handwheel to plug in the valve direction, and at the same time drive the valve plate to rotate 90 degrees, when turning the hand wheel, the plug will be under pressure, the valve opening to both sides, and the valve will be tightly pressed on the seat, the valve closed; when the hand wheel to rotate in the opposite direction, first of all, to make the plug upward movement, so that the valve on the seat out, to turn the hand wheel, driven to plug valve rotated 90 degrees, channel alignment in the body end plug channel, so that the valve is the fully open state.
Related Tags :
Ten articles before and after
Gate Valve Vs Butterfly Valve Comprehensive Compare Guide
How to Measure Butterfly Valves
What is a Double Offset Butterfly Valve
How to Fix a Leaking Butterfly Valve?
Tilting Disc Check Valve | Zecovalve Blog
working principle, design features, product performance and application use | Zecovalve Blog